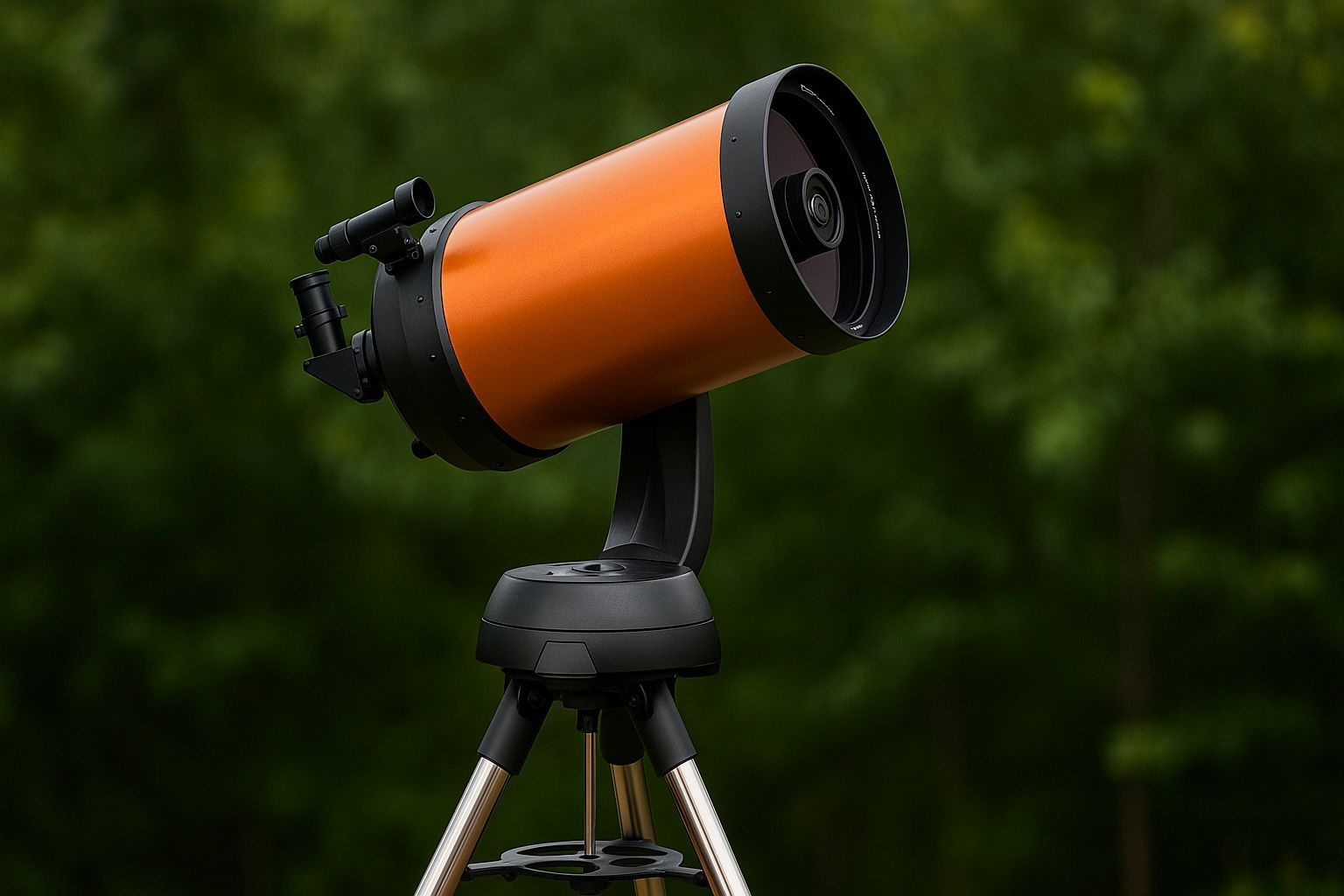
8-Inch Showdown: NexStar 8SE vs Apertura AD8 vs eVscope 2 – Classic Telescopes Battle Smart Tech in 2025
Celestron NexStar 8SE and Apertura AD8 both use 8-inch mirrors, but the 8SE features a motorized GoTo mount while the AD8 is manual. Unistellar eVscope 2, with a 4.5-inch mirror, offers real-time image stacking and automated tracking. The 8SE and AD8 require manual collimation; the eVscope 2 ships pre-aligned. As of 2025, over 10,000 smart telescopes have sold, with new models from Celestron and Unistellar on the market.