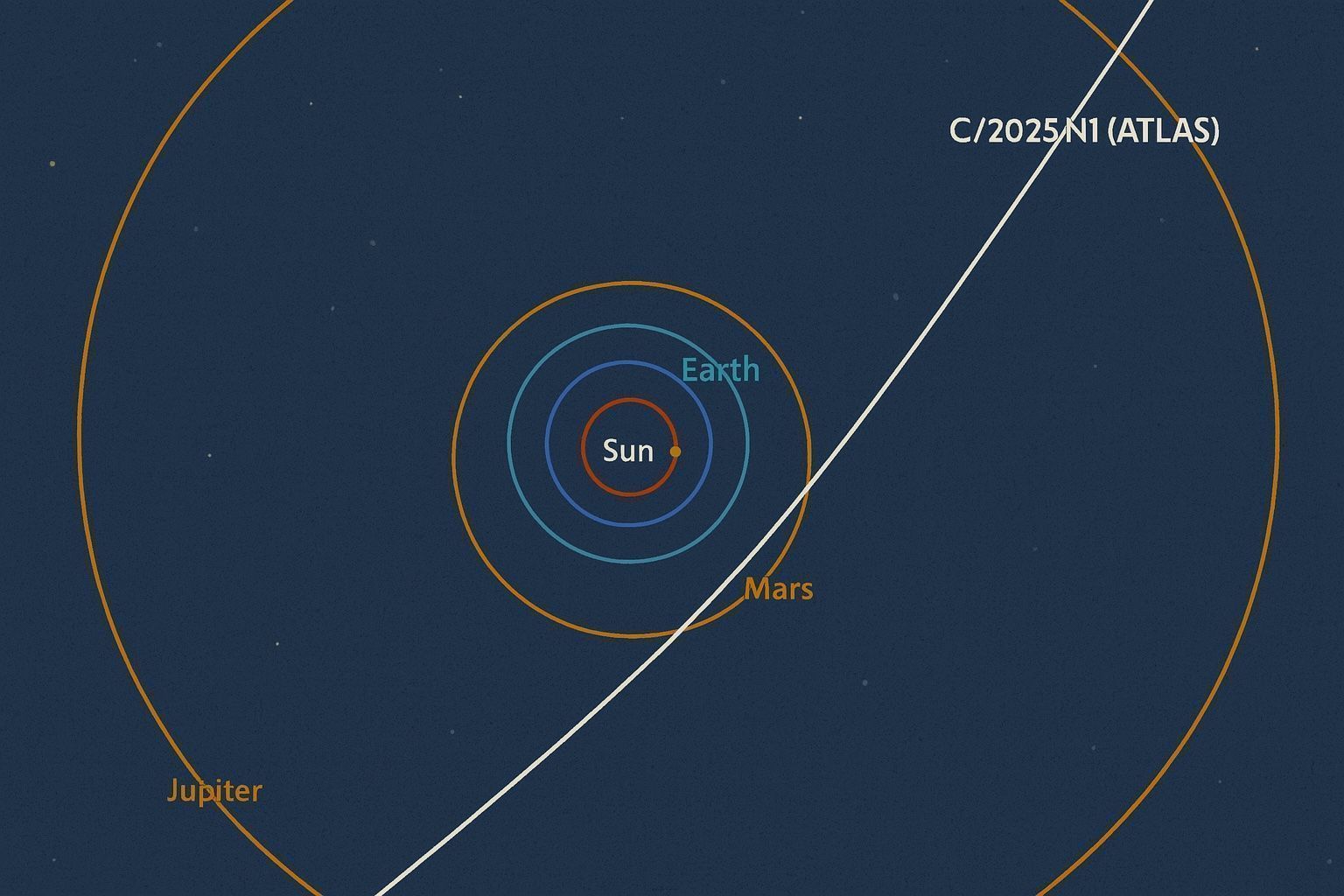
Comet 3I/ATLAS Today: Latest News, Science Updates, and How to See the Rare Interstellar Comet Before Its Dec. 19, 2025 Flyby
Updated Wednesday, Dec. 17, 2025 — Interstellar comet 3I/ATLAS (also referenced as C/2025 N1 (ATLAS)) is now just two days from its closest approach to Earth, and today’s coverage spans everything from practical skywatching advice to fresh scientific analysis of the comet’s “non‑gravitational” motion. Space+1 On Friday,